Unlock Your Medical Skills with the Ultimate Medical Simulator: The Game-Changer for Aspiring Healthcare Professionals!
What do you mean by laparoscopy simulator?
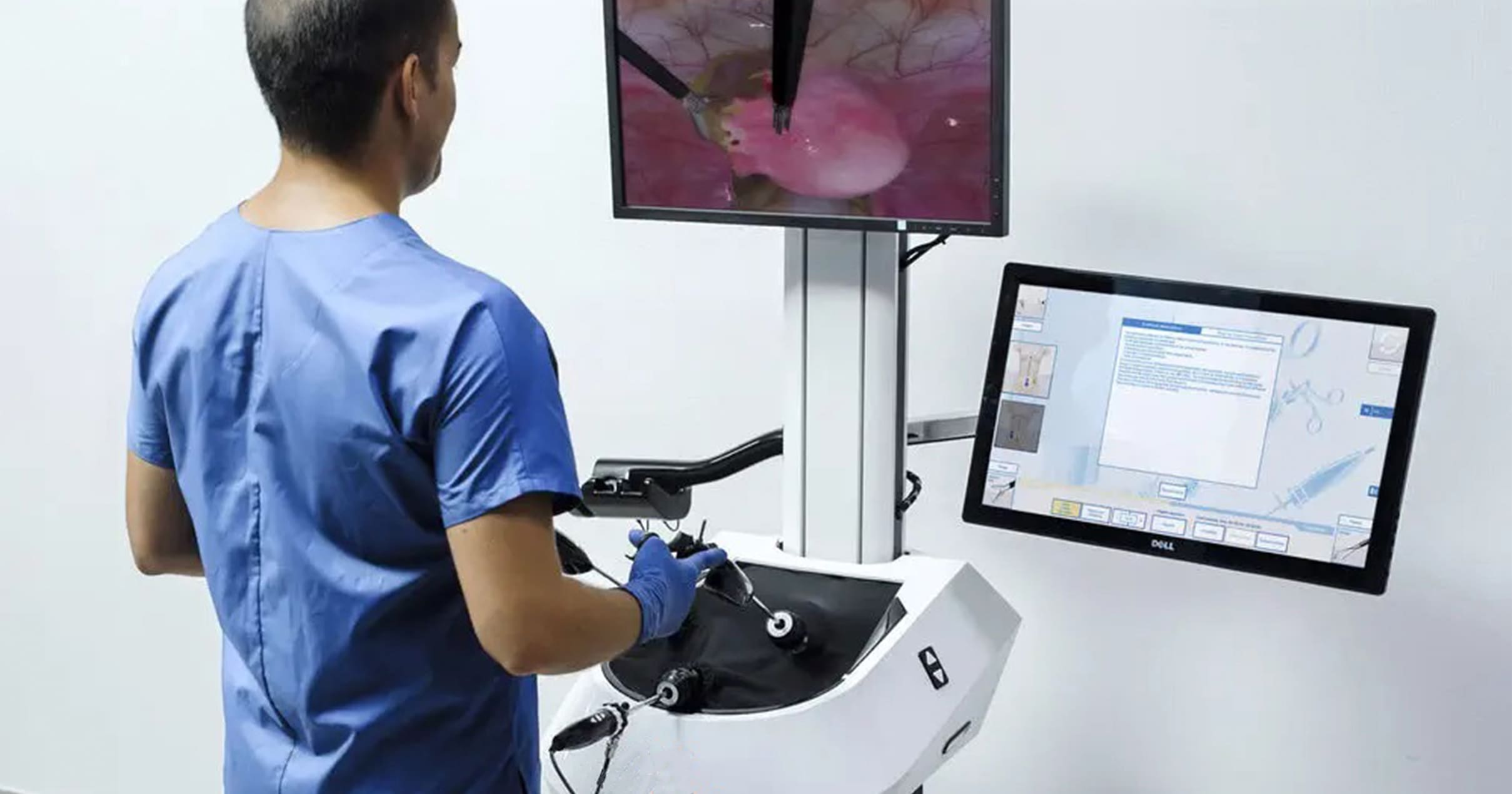
A laparoscopy simulator
is a medical training tool used to teach and practice laparoscopic surgical
procedures. Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole
surgery, involves making small incisions in the patient's body and using
specialized instruments to perform surgical procedures. These procedures are
often used in various fields of medicine, including gynecology, urology,
general surgery, and more.
Laparoscopy simulators are designed to replicate the experience of performing laparoscopic surgery in a controlled and realistic environment. They typically consist of the following components:
- Physical
Simulator: This is a physical model that mimics the anatomy of the
human body, often made of materials that mimic the texture and appearance
of organs and tissues. The simulator may include structures such as the
abdominal cavity, organs, blood vessels, and other relevant anatomical
features.
- Surgical
Instruments: Laparoscopic instruments, such as trocars, graspers,
scissors, and cameras, are used in the simulator. These instruments are
manipulated by the trainee to perform various surgical tasks.
- Camera
and Video System: Laparoscopy simulators often incorporate cameras and
video systems to provide a visual feedback loop to the trainee, similar to
what a surgeon would see during a real laparoscopic procedure. This
feedback helps users develop their hand-eye coordination and spatial
awareness.
- Computer
Software: Many modern laparoscopy
simulators are augmented with computer software that tracks the
trainee's movements and provides real-time feedback on their performance.
This feedback can include metrics on accuracy, precision, and efficiency
in completing surgical tasks.
- Haptic
Feedback: Some advanced laparoscopy simulators incorporate haptic
feedback systems that simulate the tactile sensations and resistance
encountered during real surgery. This helps trainees develop a sense of
touch and manipulation skills.
The primary goal of laparoscopy simulators is to allow
medical professionals, including surgeons and surgical residents, to practice
and refine their laparoscopic skills in a safe and controlled environment
before performing actual surgeries on patients. This training can enhance the
proficiency of surgeons and reduce the risk of errors during real surgical
procedures, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Additionally, laparoscopy
simulators are valuable for assessing and certifying the competence of surgical
trainees.
How heart and lung simulator are saving human lives?
A heart and
lung simulator, also known as a cardiopulmonary simulator or cardiac
and pulmonary simulator, is a medical training device designed to replicate the
physiological functions of the heart and lungs. These simulators are used for
medical education, research, and healthcare training purposes to help
healthcare professionals and students develop the skills necessary to diagnose
and treat cardiac and pulmonary conditions.
Components of a Heart and Lung Simulator:
- Cardiac
Module: This part of the simulator mimics the functions of the heart.
It typically includes chambers, valves, and pumps that can be controlled
to simulate various heart conditions, rhythms, and cardiac output. It allows
users to practice tasks like auscultation (listening to heart sounds),
electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation, and understanding the hemodynamics
of the cardiovascular system.
- Pulmonary
Module: The pulmonary module replicates the functions of the lungs and
respiratory system. It includes components such as airways, alveoli, and
mechanisms for simulating ventilation and respiration. Users can practice
tasks like auscultating lung sounds, interpreting chest X-rays, and
managing respiratory conditions.
- Control
System: A computerized control system is often integrated with the
simulator. This system allows instructors or users to adjust and control
parameters like heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, respiratory
rate, and other vital signs to create realistic scenarios for training.
- Feedback
Mechanism: Some advanced simulators provide real-time feedback,
including physiological data and performance metrics, to help learners
assess their skills and improve their decision-making abilities.
Uses of a Heart and Lung Simulator:
- Medical
Education: Heart
and lung simulators are valuable tools for medical and nursing
schools, as well as for the ongoing education of healthcare professionals.
They provide a safe and controlled environment for students to learn about
cardiac and pulmonary physiology, practice clinical skills, and develop
diagnostic and treatment strategies.
- Clinical
Skills Training: Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses,
respiratory therapists, and paramedics, use these simulators to enhance
their skills in diagnosing and managing cardiac and respiratory
emergencies. Simulators allow them to practice procedures like CPR,
intubation, and defibrillation.
- Research
and Development: Cardiopulmonary simulators are used in medical
research and device development. Researchers can use them to study cardiac
and pulmonary conditions, test new medical devices, and develop treatment
protocols.
- Assessment
and Certification: Simulators can be used for assessing the competency
of healthcare providers. They are often integrated into certification
programs to ensure that professionals meet the required standards for
cardiac and pulmonary care.
Overall, heart and lung simulators play a crucial role in
healthcare training and education, offering a realistic and safe environment
for healthcare professionals to gain expertise in managing cardiac and
pulmonary conditions, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.
What is auscultation simulator and its features?
An auscultation
simulator is a medical training device designed to replicate the sounds
of the human body, particularly the sounds produced by the heart, lungs, and
other organs. These simulators are used for medical education and training
purposes to help healthcare professionals, such as doctors, nurses, and medical
students, develop their auscultation skills. Auscultation is the act of
listening to internal body sounds, often using a stethoscope, to assess the
functioning of various organs and systems. Here are some key features and uses
of an auscultation simulator:
Features of an Auscultation Simulator:
- Realistic
Sound Reproduction: The primary function of an auscultation simulator
is to reproduce the sounds of the human body accurately. This includes
replicating the normal sounds of the heart, lungs, and blood vessels, as
well as abnormal or pathological sounds associated with various medical
conditions.
- Variety
of Sounds: Auscultation simulators typically offer a wide range of
sounds, including heart murmurs, lung crackles, wheezing, and other
cardiac and respiratory sounds. Some simulators may also simulate bowel
sounds or vascular sounds.
- Adjustable
Settings: Many simulators allow users to adjust parameters such as
volume, pitch, and intensity to create different clinical scenarios and
levels of complexity.
- Interactive
Feedback: Some advanced auscultation simulators provide interactive
feedback to users. They may include visual displays or software that can
help users identify and interpret the sounds they hear.
- Remote
Control: In a training or classroom setting, instructors often have
the ability to control the simulator remotely, changing the sounds or
scenarios to challenge and educate students.
Uses of an Auscultation Simulator:
- Medical
Education: Auscultation simulators are widely used in medical and
nursing education programs to train students in the art of listening to
body sounds. They help students become proficient in identifying normal
and abnormal sounds, which is crucial for making accurate diagnoses.
- Clinical Skills Training: Healthcare professionals use auscultation simulators to practice and refine their skills in assessing patients. This includes diagnosing heart conditions like murmurs, detecting respiratory disorders, and monitoring the progress of treatment.
- Assessment
and Certification: Simulators are sometimes used in certification and
competency assessments for healthcare professionals. They ensure that
clinicians can accurately and confidently perform auscultation in real
clinical settings.
- Research and Development: In the field of medical research, auscultation simulators can be used to study and document various sounds associated with different medical conditions. This research can lead to better diagnostic tools and treatment methods.
Auscultation simulators are valuable tools for medical education and clinical training because they allow learners to practice auscultation skills in a controlled and standardized manner, ensuring that healthcare providers are well-prepared to provide high-quality patient care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, medical simulators are invaluable tools in
the field of healthcare education and training. These advanced devices
replicate the intricacies of the human body, offering students, medical
professionals, and researchers a safe and controlled environment to hone their
skills, deepen their understanding, and enhance patient care. From surgical
simulators to auscultation trainers, these technologies are pivotal in shaping
competent and confident healthcare providers, ultimately leading to improved
medical outcomes and better healthcare for all. As technology continues to
evolve, the role of medical simulators in education and healthcare will only
grow, ushering in a new era of precision and proficiency in the medical field.
For more information please visit here: https://www.mavericsolution.com/



Comments
Post a Comment