Understanding Everything About Human Lung Simulators
A human lung simulator is a sophisticated medical device or software tool designed to replicate the structure and function of the human lungs for various purposes, including medical research, education, and clinical training. These simulators are valuable tools for understanding respiratory physiology, testing medical devices, and training healthcare professionals without the need for live patients.
Anatomical Replication: A human lung simulator includes a physical or digital representation of the human lung anatomy. This may involve the use of artificial lung models, 3D printed lung structures, or computer-generated anatomical models that mimic the size, shape, and structure of the human lungs.
Airway System: The simulator includes an intricate airway system that mimics the branching structure of the respiratory tract, from the trachea down to the bronchioles and alveoli. This system allows for the flow of air and gases to replicate the natural breathing process.
Mechanical Ventilation: Some simulators are equipped with mechanical ventilation systems that can simulate various breathing patterns, including normal breathing, deep breathing, shallow breathing, and even abnormal patterns seen in lung diseases. These systems can adjust factors like tidal volume, respiratory rate, and inspiration-expiration ratios.
Gas Exchange: The lung simulator should replicate the gas exchange process that occurs in the alveoli. It should be capable of simulating the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the simulated lung tissue and the surrounding environment.
Pressure and Compliance Control: Lung simulators often allow users to control factors such as airway pressure, compliance (the lung's ability to expand), and resistance (the hindrance to airflow). These parameters can be adjusted to mimic various lung conditions and responses to therapy.
Monitoring and Data Collection: Advanced lung simulators are equipped with sensors and monitoring devices to measure parameters such as airway pressure, airflow, oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, and lung compliance. This data can be used for research, training, and assessment purposes.
Pathological Scenarios: Some simulators can simulate specific lung diseases or conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). This enables healthcare professionals to practice managing these conditions.
Educational and Training Features: Lung simulators are used extensively in medical education and training programs. They can provide a platform for healthcare students and professionals to practice various respiratory procedures, such as intubation, mechanical ventilation, and bronchoscopy, in a controlled and safe environment.
Research and Development: Researchers use lung simulators to study lung physiology, test new medical devices (such as ventilators or inhalers), and develop and validate treatment protocols.
Simulation Software: In some cases, lung simulators are entirely digital, running on computer software. These software-based simulators offer a high degree of flexibility and customization for simulating different scenarios and conditions.
Human lung simulators play a crucial role in advancing
respiratory medicine, improving patient care, and enhancing the skills of
healthcare professionals. They are versatile tools that can be adapted for
various applications, from medical research and development to clinical
training and education.
what do you
understand by neonatal and pediatric lung simulator?
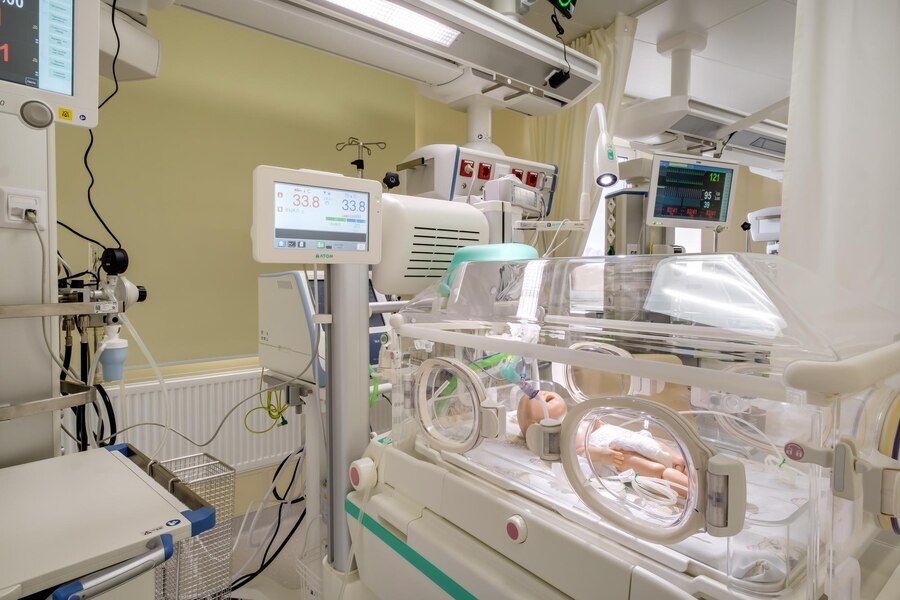
A neonatal and pediatric
lung simulator is a specialized medical device or software tool
designed to replicate the structure and function of the lungs in newborns
(neonates) and children (pediatric patients). These simulators are tailored to
mimic the unique respiratory physiology and characteristics of infants and
young children. They serve several important purposes in the medical field,
including medical training, research, and device testing.
- Age-Specific Simulation: Unlike adult lung simulators, which replicate the anatomy and function of adult lungs, neonatal and pediatric lung simulators are designed to accurately represent the smaller size, anatomy, and respiratory mechanics of infants and children. They account for the differences in lung compliance, airway resistance, and gas exchange seen in younger patients.
- Training
and Education: Neonatal and pediatric lung
simulators are crucial for training healthcare professionals,
including neonatologists, pediatricians, respiratory therapists, and
nurses, in the management of respiratory conditions and procedures
specific to infants and children. These simulators enable healthcare
providers to practice techniques like neonatal resuscitation, mechanical
ventilation, and airway management on a lifelike model without putting
real patients at risk.
- Research
and Development: Researchers and medical device manufacturers use
these simulators to develop and test medical equipment and interventions
tailored for neonatal and pediatric patients. This includes evaluating the
performance of neonatal ventilators, inhalers, and other respiratory
devices in realistic scenarios.
- Pathological
Scenarios: Neonatal and pediatric lung simulators can simulate various
respiratory conditions commonly seen in infants and children, such as
respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), bronchiolitis, asthma, and congenital
anomalies. Healthcare professionals can practice managing these conditions
in a controlled environment.
- Size
and Physiology Considerations: These simulators account for the
smaller lung volumes, higher respiratory rates, and unique physiological
responses of neonates and pediatric patients. They may also incorporate
features like realistic lung compliance, airway resistance, and gas
exchange properties.
- Monitoring
and Data Collection: Just like adult lung simulators, neonatal and
pediatric versions often come equipped with monitoring devices and sensors
to measure parameters such as airway pressure, airflow, oxygen saturation,
and carbon dioxide levels. This data helps assess the effectiveness of
interventions and treatments.
- Safety
and Ethical Considerations: Using neonatal and pediatric lung
simulators ensures the safety of real patients, particularly vulnerable
newborns and children. It also addresses ethical concerns related to conducting
medical training and research on young patients.
In summary, neonatal and pediatric lung simulators are
specialized tools tailored to the unique respiratory needs and characteristics
of infants and children. They play a vital role in medical education, research,
and device development, ultimately contributing to improved care and outcomes
for young patients with respiratory conditions.
Auscultation is a medical procedure where healthcare
professionals listen to internal body sounds, such as the heartbeat, breath
sounds, and bowel sounds, using a stethoscope or other listening devices.
If "Matta auscultation" is an infant
lung simulator term or concept that has emerged or gained relevance
after my last update, I recommend consulting current medical literature or
speaking with a healthcare professional for the most up-to-date and accurate
information regarding this topic.
For more Information Please visit here: https://www.mavericsolution.com/



Comments
Post a Comment